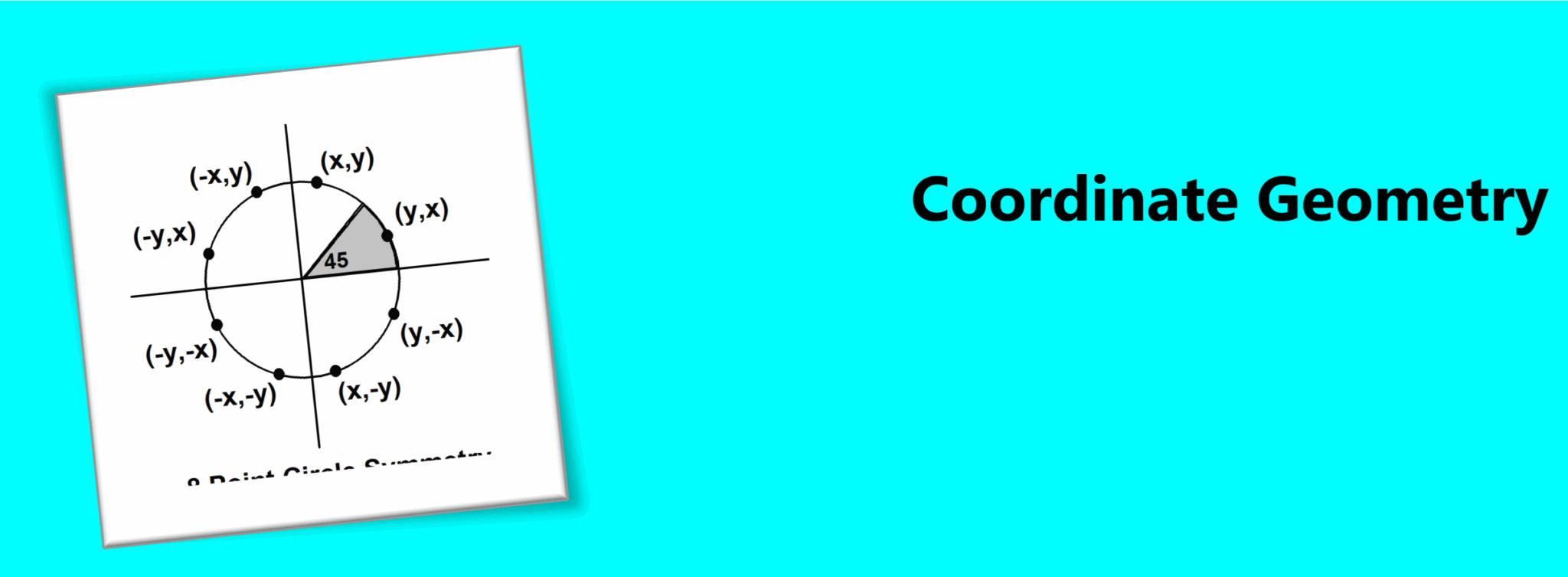
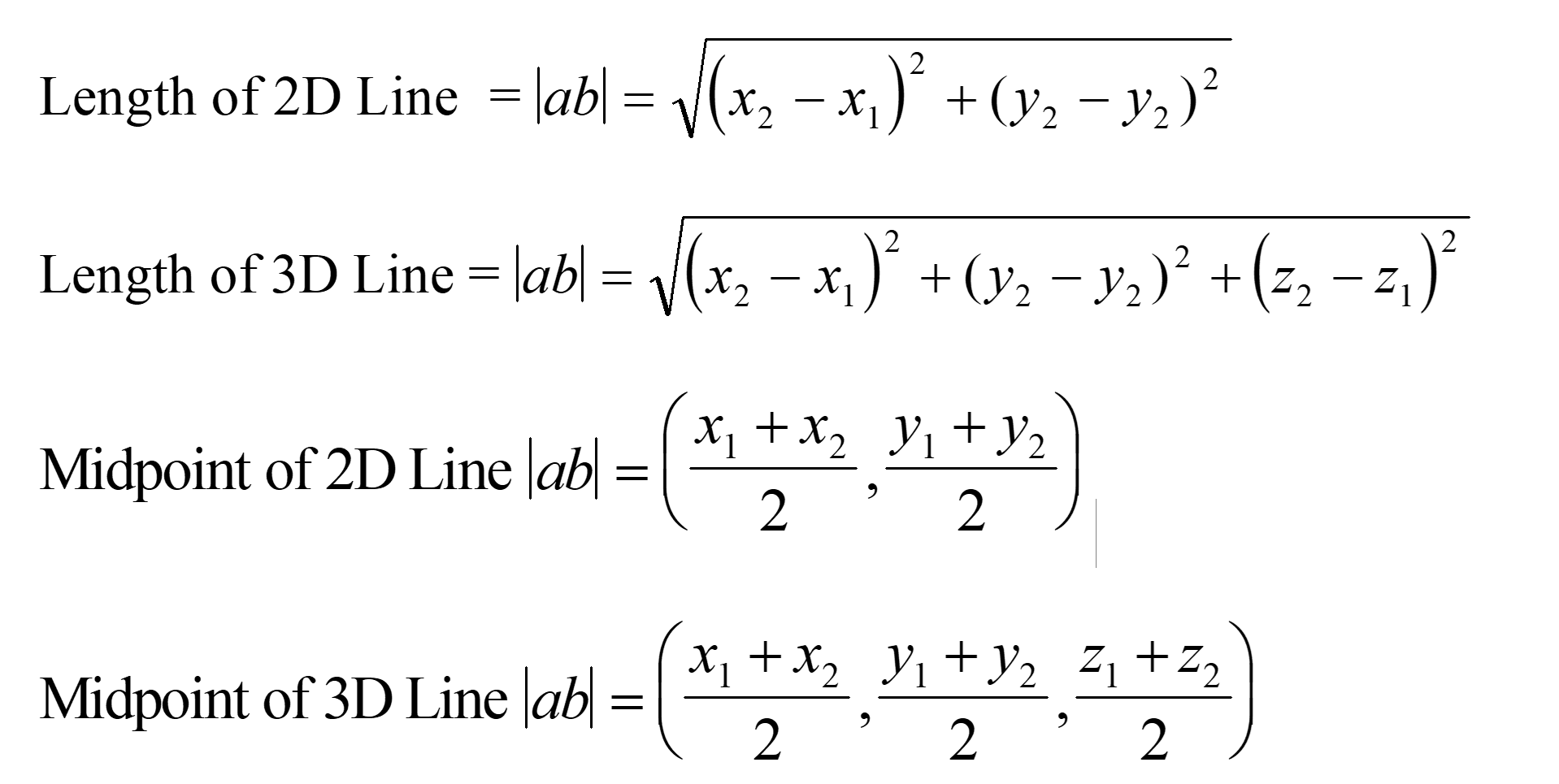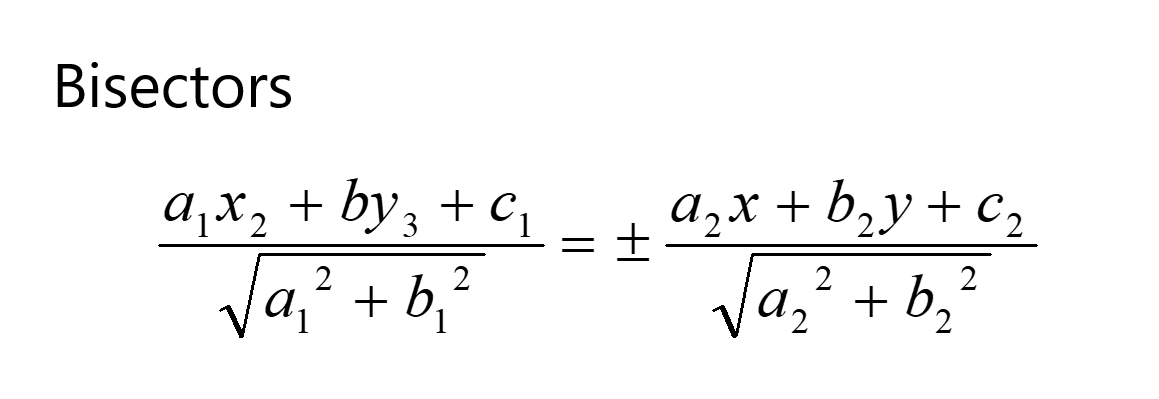Coordinate Geometry Lines
Here we cover the reference functions useful for 2D and 3D coordinate geometry.
As you learn more about computer and vector graphics these basic mathematical formulas will become part of your toolbox.
How to calculate the length of a line and its midpoint. 3d and 2d Graphics versions
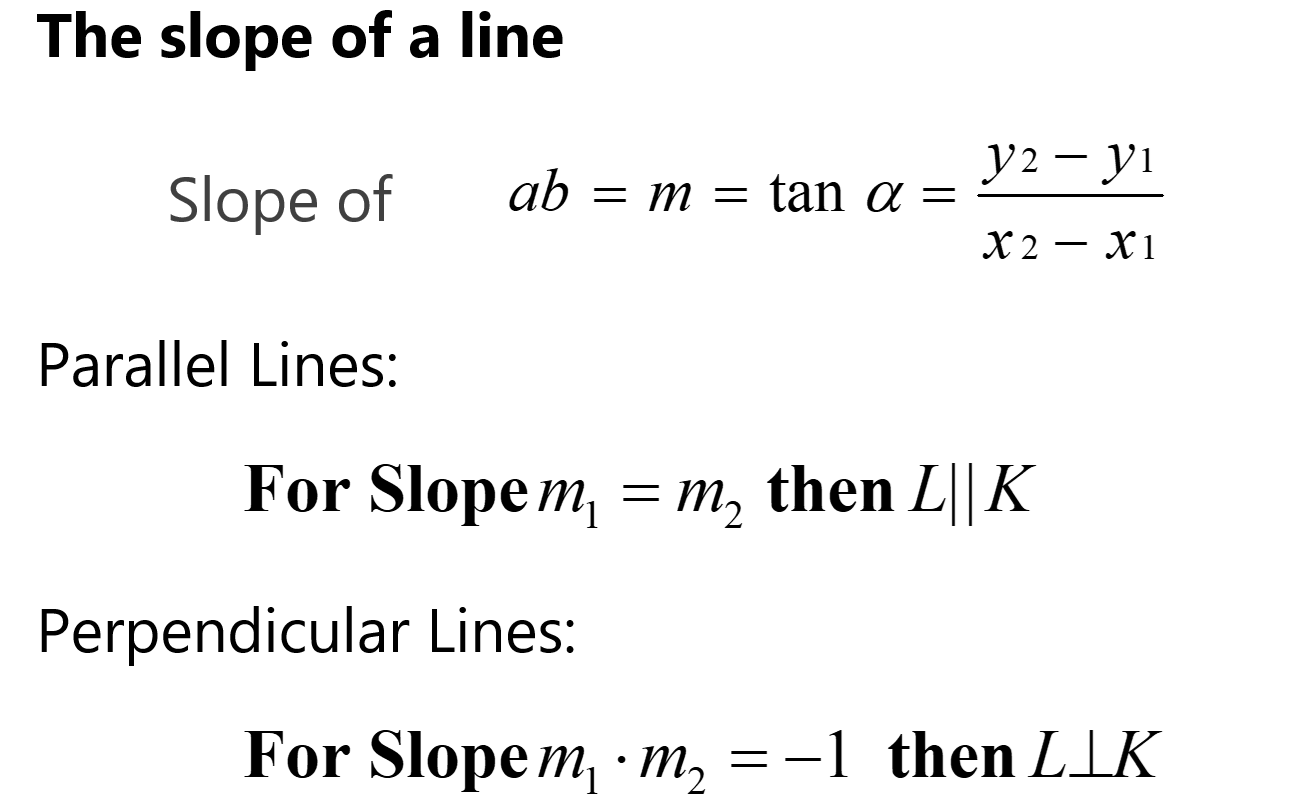
The Slope of a Line : Coordinate Geometry Lines
The slope of a line is a measure of its steepness and direction. It is calculated as the ratio of the vertical change (rise) to the horizontal change (run) between two points on the line.
Parallel Lines
Parallel lines have the same slope. If two lines are parallel, their slopes are equal.
Perpendicular Lines
Perpendicular lines intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). The slopes of two perpendicular lines are negative reciprocals of each other.
General Equation of the line
y – y1 = m ( x – x1 )
If it cuts (0,c) then it becomes y = mx + c
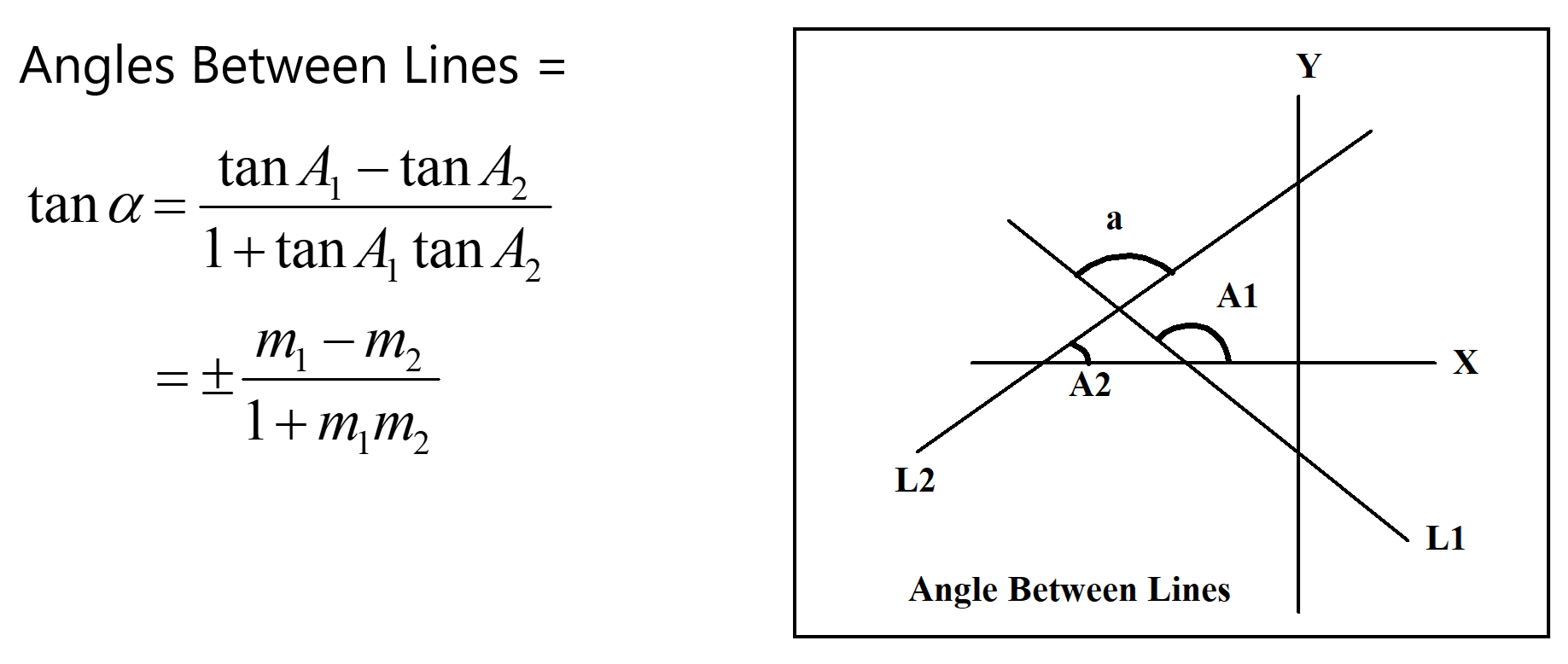
BISECTORS
The bisector of an angle formed by two intersecting lines is a line that divides the angle into two equal parts. The equation of the angle bisector can be derived using the properties of the lines and the angle they form.
Coordinate geometry provides a powerful framework for analyzing and solving geometric problems using algebraic methods. Understanding the properties and equations of lines is fundamental to mastering this area of mathematics.
Partner Advertising